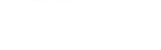CHAMARAJASAGARA DAM/RESERVOIR PROFILE
About Chamarajasagara:
Chamarajasagara reservoir is formed by building a dam at Thippagondanahalli, at the confluence of Arkavathi and Kumudvathi rivers, a few kilometres away from the Silicon Valley of India, Bengaluru. Built to serve the drinking water needs of Bengaluru city, the dam can impound 3.3Thousand Million Cubic-feet (TMC) of water. It is the largest reservoir in the Arkavathi river basin in terms of capacity. It is located in the districts of Bengaluru Urban and Bengaluru Rural.
In operation since 1934, the reservoir went from being Bengaluru’s source of water to Bengaluru’s sink for wastewater. Heavily polluted the reservoir water is not used for drinking since 2012. Presently, it is being restored to hold 1.7 TMC of Netravathi river water via the Yettinahole Integrated Drinking Water project
About Profile: (Click image to launch profile)
The profile contains relevant information about Chamarajasagara Dam/Reservoir (a.k.a Thippagondanahalli Dam), in an easily readable infographic format. It gives data on: Location, Elevation, Catchment area, Catchment rainfall, Population, Seismic zone risk, Height of the dam, Storage capacity of the dam, Submergence area, Purpose and Current use of the dam, Responsible government agency, Birds, Sedimentation %, Designed utilization, and Actual utilization. It explains the thirteen threats to the dam including aging dam infrastructure and climate change.
Most importantly, it brings in the data transparency aspect. Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB), the agency responsible, is a completely opaque organization. It makes no voluntary disclosure about the important aspects of the dam on its website. Besides, the data obtained via RTI, currently processed by us, is not standing up to scrutiny.
Click the image to launch the profile. Check out our Arkavathi River Basin Map for spatial understanding of Chamarajasagara Dam.
RIVER BASIN
DAMS & FLOW
POLLUTION
GROUNDWATER
STRAWS

RAINFALL FLOODS & DROUGHT

RESTORATION